shoulder labral tear test hip|hip labrum tear recovery without surgery : supermarket To diagnose a hip labral tear your doctor will review your medical history, conduct a physical exam, and order one or more imaging tests. As a first step toward making a diagnosis, your doctor will ask about your symptoms . 4 de out. de 2016 · Assine o nosso canal: é de graça! http://bit.ly/2dern4CTem vídeo novo toda semana. | Mande perguntas para A Boca!
{plog:ftitle_list}
webLivia Jacob is on Facebook. Join Facebook to connect with Livia Jacob and others you may know. Facebook gives people the power to share and makes the world more open and connected.
The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear. See moreThe acetabulofemoral (hip) joint is the largest and most stable joint in the human body. The acetabular labrum is a soft-tissue structure . See more
Step 1:The patient should be lying supine with their head supported and both arms rested to their side in a comfortable position. Step 2:The . See more The O’Brien test is a simple procedure that healthcare professionals use to assess shoulder pain. It can detect a cartilage (labral) tear or an acromioclavicular (AC) joint . To diagnose a hip labral tear your doctor will review your medical history, conduct a physical exam, and order one or more imaging tests. As a first step toward making a diagnosis, your doctor will ask about your symptoms . A hip labral tear involves the ring of cartilage (labrum) that follows the outside rim of the hip joint socket. Besides cushioning the hip joint, the labrum acts like a rubber seal or gasket to help hold the ball at the top of the .
treatment for labral tear in hip
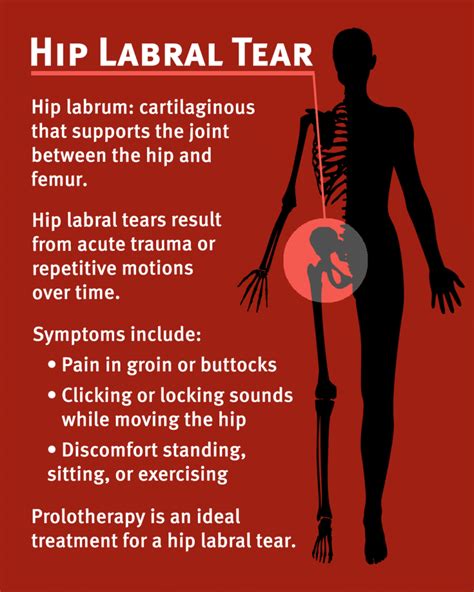
A labral tear happens when the labrum, a soft tissue ring around joints like your shoulder or hip, gets hurt or damaged. If you have a labral tear, you might have symptoms like joint pain, .
us drop covid testing travel
The physical exam will likely involve moving your leg, and especially your hip joint, into various positions to check for pain and evaluate your hip's range of motion. He or she .Labral tears cause groin pain or pain in the anterior side of the hip, and less commonly buttock pain. [1] . This mechanically induced pathology is thought to result from excessive forces at the hip joint.
Diagnosing Labral Tears of the Shoulder. To evaluate for a possible shoulder labrum tear, a Penn orthopaedic specialist will examine your shoulder, conduct several physical tests to check your range of motion, take a full health history .Symptoms of a Hip Labral Tear. A hip labral tear can be difficult to diagnose. Typical symptoms can include: Hip/groin pain. Pain is usually increased with athletics or physical activity. Pain .Symptoms and Causes. What are hip labral tear symptoms? The most common symptoms of a labral tear in your hip include: Hip pain (especially when you bend, move, exercise or play .
The least invasive hip labral tear test available is the FABER test, which stands for flexion, abduction, and external rotation. This test can often assist in diagnosing patients with a hip labral tear. What’s the Purpose of the .Shoulder Labrum Repair; Hip Microfracture Surgery; Hip Surgery; Arthroscopic Bankart Repair; Overview; . A hip labral tear occurs when the labrum of the hip tears or detaches from the rim of the acetabulum. Tears can affect any part of .Repairing a hip labral tear may involve removing frayed pieces of labrum, stitching the tear back together or using tissues from other parts of the body to replace a missing piece of labrum. If your labral tear was caused by a hip .The results of these physical tests will help your doctor decide if additional testing or imaging of your shoulder is necessary. Imaging Tests. X-rays. X-rays provide clear pictures of dense structures, like bone. The labrum of the shoulder is made .
The FADIR test is commonly used in the assessment of hip pathology, espeially femoroacetabular impingement and labral tear. However, due to high sensitivity and low specificity of the test, it is important to understand its limitations and consider its role in conjunction with other tests and diagnostic tools when assessing hip pathology [1] .Weakness in the shoulder. Hip labral tear symptoms Groin pain that may radiate to the buttocks or thigh. Pain with weight-bearing activities, such as walking or running. . Your doctor will assess the range of motion and stability of the joint and perform specific maneuvers to test for labral tears. They may apply pressure or manipulate the . A hip labral tear rarely occurs by itself. In most cases, other structures within the hip joint also have injuries. X-rays are excellent at visualizing bone. They can check for arthritis and for structural problems.
Purpose [edit | edit source]. The purpose of O'Brien's test also known as the Active Compression Test is to indicate potential labral (SLAP Lesion) or acromioclavicular lesions as cause for shoulder pain.Technique [edit | edit source]. With the patient in sitting or standing, the upper extremity to be tested is placed in 90° of shoulder flexion and 10-15° of horizontal adductionThis test also called labral crank test or compression rotation test is used to identify glenoid labral tears and assess an unstable superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) lesions. . load is applied along the axis of the humerus with one hand while the other hand performs humeral rotation while the shoulder is being elevated in the .
A hip labral tear is damage to the cartilage that lines and protects your hip socket. Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) is the most common cause. . A healthcare provider will diagnose a hip labral tear with a physical exam and some tests. They’ll examine your hip and ask you about your symptoms. Tell your provider when you first noticed .Hip labral tear test 1: Twist test 1 O’Connor FG, Wilder RP, Nirschl R, eds. Running Medicine. Second edition. Healthy Learning; 2014. Save Show Transcript Initial position: The patient stands in front of the examiner, keeping the feet shoulder-width apart, and holding the examiner’s hands for support. Initiate hip joint movement: The . Type 1: In this type of tear, your labrum shows signs of fraying or shredding but still functions. Type 1 tears are often seen in people who are middle-aged or older. Type 2: This is the most common SLAP tear type. In Type 2 tears, the labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder socket. Type 3: Torn labrum tissue is caught in the .There are several types of labral tears: A SLAP lesion (superior labrum, anterior [front] to posterior [back]) is a tear of the labrum that usually occurs on the upper part of the socket and may also involve the origin, or starting point, of the long head of the biceps tendon.; A tear of the front part of the labrum at the bottom of the socket is called a Bankart lesion.
Osteoarthritis of the hip, a degeneration of the cartilage, which can lead to rough, bone on bone contact in the hip. What does a hip labral tear feel like? Hip labral tear symptoms can include: Deep groin pain or pain in the buttocks on the side of the injured hip. A feeling or sound of clicking or locking when your hip is in motion. Superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) tears are a subset of labral pathology in acute and chronic/degenerative settings. First described in the 1980s, extensive study has followed to elucidate appropriate evaluation and management.[1] Patient-specific considerations and appropriate utilization of both non-surgical and surgical interventions are of the utmost .
Hip pain is common in adults of all ages and activity levels. In nonelite adult soccer players, hip and groin injuries represent 28% to 45% of all injuries in women and 49% to 55% in men. 1 The . Labral tear is generally secondary to femoroacetabular impingement, trauma, dysplasia, capsular laxity, and degeneration. Patients with labral tear complain about anterior hip or groin pain most commonly with a most consistent physical examination called positive anterior hip impingement test. Magne . Ongoing shoulder pain or other symptoms should prompt a visit to your doctor. After a physical exam, your doctor will likely order some tests. There is no specific shoulder labrum tear test, such as by moving your shoulder a certain way. Instead, doctors rely on imaging exams and sometimes, arthroscopy, to diagnose the problem. X-rays can show . Your healthcare provider can use specific examination tests to help determine the cause of your hip pain. X-rays of the hip are typically normal but should be checked to evaluate for other possible causes of pain. An MRI test is helpful in evaluating the labrum, but may not always show the labrum clearly. Injecting contrast fluid into the hip joint at the time of the MRI .
The exam of the shoulder has to be completed by some specialized tests and provocative maneuvers that are specific for different shoulder lesions and pathologies. These tests will help us confirm or exclude the presence of a specific shoulder condition, that we may only suspect after the inspection and the assessment of the full range of motion.A hip labral tear occurs when there is damage to the ring of cartilage (labrum) along the outside rim of the socket of your hip joint. Falls or the wear and tear of repetitive activities are common causes of this injury. . Tests. Physical examination Your doctor will conduct a complete physical examination and collect your health history to .
A hip labral tear is a tear in the tissue that lines the hip joint. This tissue plays a very important role in hip function and mobility, so injuring it can cause significant pain. Without treatment, a hip labral tear can also lead to joint degeneration, or osteoarthritis. If someone already has osteoarthritis in the hip, sustaining a hip .In the event of a-c joint pathology the patient will likely complain of pain in both positions of the test. Accuracy of Test. Accuracy of this test is questionable but is improved when coupled with additional tests such as the Speed’s Test and Yergeson’s Test as well as the Crank or Anterior Apprehension Test. A posterior labral tear is referred to as a reverse Bankart lesion, or attenuation of the posterior capsulolabral complex, and commonly occurs due to repetitive microtrauma in athletes. Diagnosis can be made clinically with positive posterior labral provocative tests and confirmed with MRI studies of the shoulder.
Hip labral tears are common in athletes or those who put immense strain on their hip joints. Dr. Daniel Gibbs provides some of the most highly-regarded hip labral tear treatment available today in Park City Utah. What is a Labral Tear? The labrum is a ring of cartilage that cushions and steadies your hip joint.Diagnosing a posterior labral tear of the shoulder can be difficult for physicians. These tears can present with a wide variety of symptoms and there are multiple physical exam tests of undetermined significance. Posterior shoulder instability is less commonly seen than anterior instability and the incidence is 2-5% (3).
Shoulder & Elbow Filters Recent cases . A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. . provocative tests. anterior labral tear. pain if hip is brought from a fully flexed, externally .
3 de ago. de 2022 · Learn three ways to enjoy FH5 on your Android or iOS device: Xbox Cloud Stream, Remote Play, or Third-party injection. Follow the steps and links provided .
shoulder labral tear test hip|hip labrum tear recovery without surgery